Neal McCluskey
Today, the Biden administration launched a new website for student debtors to enroll in its next big effort to reduce their repayments. Biden’s Saving on a Valuable Education (SAVE) plan seeks to make income‐driven repayment (IDR) much more generous than it has been. IDR is intended to ease repayment burdens when debtors aren’t earning very much. It does this by pegging repayment requirements to income rather than set, monthly payments. Also, if a borrower has debt remaining after 20 or 25 years of repayment it will be forgiven, with the time spans depending on whether the debt was just for undergraduate education or also grad school.
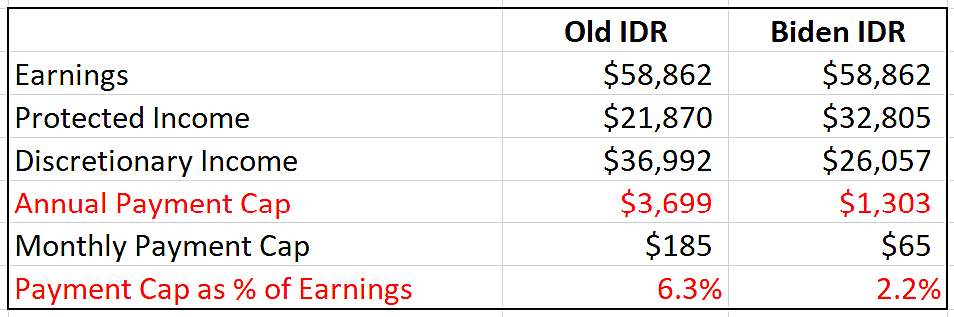
There are many possible calculations to show the effect of SAVE based on different combinations of education consumed, debt levels, family size, and earnings, which I will eventually take up. But to quickly illustrate how much more generous SAVE is than previous IDR, we can look at repayment requirements for a single, recent bachelor’s graduate with an average new grad’s salary of $58,862.
The key IDR changes are:
The amount of income incurring no charge (“protected income”) rises from 150 percent of the federal poverty level to 225 percent.
Payment drops from 10 percent of the difference between earnings and protected income (“discretionary income”) to 5 percent.
As you can see in the table below, these changes make a substantial difference, dropping the annual repayment cap from $3,699 to $1,303 and monthly charges from $185 to $65. Basically, a two‐thirds repayment reduction.
Importantly, IDR before the change allowed for relatively painless repayment. The rule of thumb is that to be comfortably repaid, student debt should not exceed 8 percent of one’s earnings. Before SAVE, the annual payment constituted only 6.3 percent of earnings. Under the new plan, it is only 2.2 percent.
This is very generous with taxpayers’ dollars, especially considering that the name of the plan itself says borrowers’ education was valuable, presumably to them. It is also of dubious legality, with the executive branch unilaterally changing basic lending terms. It’s not quite as egregious as POTUS simply declaring mass debt cancellation, but it still stretches executive power well beyond what it should be.